前言
前阵子看有师傅在公众号上发表了Resin解析漏洞分析,我们也知道有个常用的OA用的就是Resin,因此我认为了解它的漏洞是十分必要的。
原理分析
这个漏洞和IIS解析漏洞比较像,可以通过创建一个xxx.jsp的文件夹,并在其中放置一个txt文件,文件的内容将会被当作JSP解析。
我认为要分析这个漏洞原理,首先得先了解访问jsp文件时Resin是如何处理我们请求的。
首先看下*.jsp是被哪个Servlet处理的,从配置app-default.xml中可以看出,我们的请求会被com.caucho.jsp.JspServlet处理。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| <servlet servlet-name="resin-jsp"
servlet-class="com.caucho.jsp.JspServlet">
<init>
<load-tld-on-init>false</load-tld-on-init>
<page-cache-max>1024</page-cache-max>
</init>
<load-on-startup/>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping url-pattern="*.jsp" servlet-name="resin-jsp" default="true"/>
|
本来以为在JspServlet下断点可以看到请求调用栈,但是在实际操作的过程中发现并没有执行到JspServlet中的方法就返回了,确实比较奇怪。
在Resin中发起HTTP请求一定会经过HttpRequest#handleRequest方法处理,可以在这个方法中打断点排查问题,经过排查发现在PageFilterChain#doFilter中就完成了JSP的”编译”和执行工作,这点比较奇怪,因为之前分析Tomcat中”编译JSP”的操作是在servlet中完成的。所以其实针对Resin对JSP文件处理的分析重点就在PageFilterChain#doFilter中。
JSP编译后会被封装到Page对象中,而Page对象的引用被保存以pageRef属性中,因此首先检测pageRef是否为空,如果是则直接通过 page.pageservice(req, res);执行请求,不经过后面编译的逻辑。- 如果缓存中没有
page对象,则通过compilePage编译JSP并封装为Page对象返回,new SoftReference创建引用对象,再通过pageservice执行请求。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
| public void doFilter(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException
{
HttpServletRequest req = (HttpServletRequest) request;
HttpServletResponse res = (HttpServletResponse) response;
FileNotFoundException notFound = null;
SoftReference<Page> pageRef = _pageRef;
Page page;
if (pageRef != null)
page = pageRef.get();
else
page = null;
if (page == null || page._caucho_isModified()) {
try {
_pageRef = null;
page = compilePage(page, req, res);
if (page != null) {
_pageRef = new SoftReference<Page>(page);
_isSingleThread = page instanceof SingleThreadModel;
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
page = null;
notFound = e;
}
}
if (page == null) {
if (notFound == null)
return;
String errorUri = (String) req.getAttribute(RequestDispatcher.ERROR_REQUEST_URI);
String uri = (String) req.getAttribute(RequestDispatcher.INCLUDE_REQUEST_URI);
String forward = (String) req.getAttribute(RequestDispatcher.FORWARD_REQUEST_URI);
if (uri != null) {
throw notFound;
}
else if (forward != null) {
throw notFound;
}
else if (errorUri != null) {
throw notFound;
}
else {
log.log(Level.FINER, notFound.toString(), notFound);
}
((HttpServletResponse) res).sendError(HttpServletResponse.SC_NOT_FOUND);
}
else if (req instanceof HttpServletRequest) {
try {
if (_isSingleThread) {
synchronized (page) {
page.pageservice(req, res);
}
}
else
page.pageservice(req, res);
} catch (ServletException e) {
...
}
|
Page#pageService-->JavaPage#service-->_aaa#_jspService,最后通过JSP生成类的_jspService方法完成请求。
如何进入PageFilterChain?
通过上面的分析我们可以知道,在PageFilterChain中完成了对JSP的编译和执行,所以我们分析的重点就在于如何才能进入PageFilterChain中?
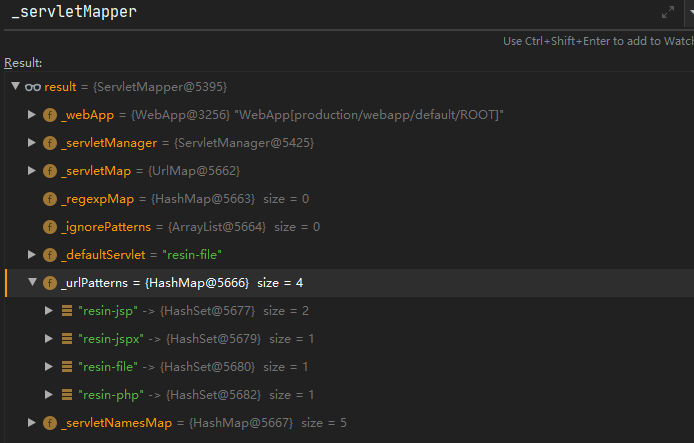
追踪创建PageFilterChain的过程,在WebApp#buildInvocation中,完成了PageFilterChain的创建,我摘了部分代码分析。
- 首先从缓存中获取
FilterChains,如果有的话则直接获取chains,缓存中保存的Chains和URL有关。
- 如果缓存没有,则通过
_servletMapper.mapServlet(invocation);获取Chains。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
| public Invocation buildInvocation(Invocation invocation, boolean isTop)
{
...
else {
FilterChainEntry entry = null;
String query = invocation.getQueryString();
boolean isCache = true;
if (query != null && query.indexOf("jsp_precompile") >= 0)
isCache = false;
else if (_requestRewriteDispatch != null)
isCache = false;
if (isCache)
entry = _filterChainCache.get(invocation.getContextURI());
if (entry != null && ! entry.isModified()) {
chain = entry.getFilterChain();
invocation.setServletName(entry.getServletName());
if (! entry.isAsyncSupported())
invocation.clearAsyncSupported();
invocation.setMultipartConfig(entry.getMultipartConfig());
} else {
chain = _servletMapper.mapServlet(invocation);
...
}
|
在mapServlet中,主要做了下面的操作
- 从
ServletInvocation中获取URL并去除;xxx的内容
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| String contextURI = invocation.getContextURI();
try {
cleanUri = Invocation.stripPathParameters(contextURI);
} catch (Exception e) {
log.warning(L.l("Invalid URI {0}", contextURI));
return new ErrorFilterChain(404);
}
|
1
| ServletMapping servletMap = _servletMap.map(cleanUri, vars);
|
- 如果根据URL没有匹配到
Servlet处理则根据URL获取资源内容,并设置使用_defaultServlet处理。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| servletName = servletMap.getServletName();
if (servletName == null) {
try {
InputStream is;
is = _webApp.getResourceAsStream(contextURI);
if (is != null) {
is.close();
servletName = _defaultServlet;
}
} catch (Exception e) {
}
|
- 如果URL以
j_security_check结尾则使用j_security_check作为Servlet
1
2
3
| if (matchResult == null && contextURI.endsWith("j_security_check")) {
servletName = "j_security_check";
}
|
- 如果匹配成功则设置
servletPath和servletName等属性到invocation对象中,根据Servletname从_servletManager获取ServletConfigImpl对象,创建FilterChains
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| ArrayList<String> vars = new ArrayList<String>();
vars.add(contextURI);
String servletPath = vars.get(0);
invocation.setServletPath(servletPath);
invocation.setServletName(servletName);
ServletConfigImpl newConfig = _servletManager.getServlet(servletName);
FilterChain chain= _servletManager.createServletChain(servletName, config, invocation);
|
所以这个漏洞的重点在于为什么/test.jsp/xxx.txt可以被 _servletMap.map(cleanUri, vars);匹配到。
进入到UrlMap#map中,发现默认情况下*.jsp会交给^.*\.jsp(?=/)|^.*\.jsp\z正则处理。
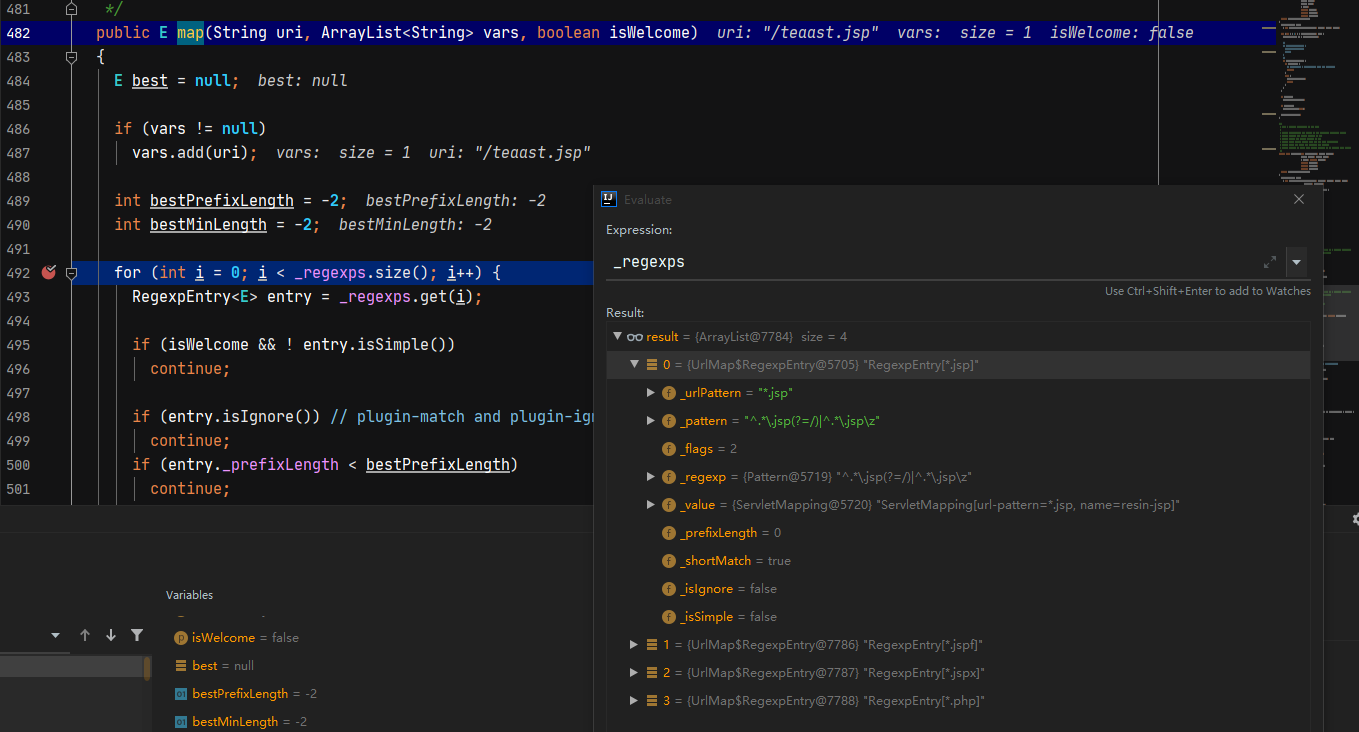
主要出问题的是^.*\.jsp(?=/)部分,这个正则的逻辑是匹配xxxx.jsp/xxxx所以我们传入的路径会被匹配到,这也是这个漏洞的本质原因。
总结
其实我认为Resin这么写可能对作者来说这本身是个正常功能,因为之前Resin也实现了Invoker的功能,可以直接根据路径加载任意类。
参考


